neoplasia in cats bladder
Symptoms of cat bladder cancer may be identified and the tumor may be removed provided it hasnt spread and it is located in an area of the bladder that can be operated on. IHC is characterised by mild to moderate hypercalcaemia normophosphataemia and an appropriate parathyroid response ie PTH.

Bladder Cancer In Cats Innovet Pet
Chronic urinary tract infection UTI.

. Neoplasia of the Urinary tract. Surgical and additional chemotherapyradiotherapy. In a review of 27 cats with bladder neoplasia 15 were diagnosed as carcinoma five were sarcoma five were benign leiomyomas or fibromas and two were lymphoma.
Brearley MJ Thatcher C Cooper JE. Start studying Week 1. There are several types of bladder tumours in cats transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most common other types include benign mesenchymal tumours squamous cell carcinoma rhabdomyosarcoma and lymphoma.
Bacterial in 65-75 cases. The diagnosis is made by excluding other causes. Transitional cell carcinoma is the common cancer of the bladder or urethra in dogs and cats accounting for 5075 of all bladder tumors.
Surgical resection by partial segmental resection is the treatment of choice. Epithelial most common or connective tissue. Only 47 cases of urinary bladder neoplasia have been reported in the cat.
In dogs the urinary bladder is also the most common site of neoplasia in the entire urinary system including both upper and lower urinary tracts and in cats the urinary bladder is the second most common site of neoplasia in the urinary tract after renal. This is a malignant cancer usually arising from the inside surface of the urinary bladder or urethra and less commonly from the muscular wall of the urinary tract. The common clinical signs seen with bladder cancer are those referable to the urinary tract.
A distinguishing feature of all squamous cell carcinomas and most. Neoplasms of the canine and feline urinary bladder are diagnostic and therapeutic challenges to the veterinary clinician. Megacolon occurs more frequently in cats than dogs and is usually seen in middle-aged to geriatric cats.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Renal Bladder and Urethra in Cats. The diagnosis of a urinary bladder neoplasm is generally delayed because of a lack of overt clinical signs or a partial response to empirical treatment. One study reported on the histopathological diagnosis of 20 urinary bladder neoplasms in cats and findings included angioma intravenous leiomyoma adenocarcinoma squamous cell carcinoma TCC leiomyosarcoma hemangiosarcoma lymphoma and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.
The cat was reported to be incontinent and treatment was declined by the owners. There is a higher incidence in humans who work in chemical industries and it is speculated chemicals in flea and tick. Hematuria stranguria dysuria pollakiuria are common presenting signs.
The usual treatment for primary ureteral neoplasia is nephrectomy and ureterectomy. Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a malignant aggressive and metastasizing spreading cancer arising from the transitional epithelium the highly stretchable lining of the urinary tract system of the kidney ureters the tubes that carry fluid from the kidneys to the bladder urinary bladder. The ascending transverse and descending colon are chronically large in diameter and filled with dry stool.
Most common tumor type. Neoplasms of the ureters bladder and urethra are uncommon in dogs and rare in cats. A case of feline rectal prolapse which appeared to be secondary to transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is described.
The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma. Cats of any age can be affected. Epithelial tumors in particular TCC are the most common tumors of the urinary bladder and account for up to 92 of feline bladder tumors Other urinary bladder tumors include SCC ADC rhabdomyosarcoma FSA CSA leiomyosarcoma HSA chemodectoma and benign tumors such as leiomyoma and fibroma.
Clinical signs and ancillary testing. The exact etiology is unknown. Urinary bladder tumors are rare in cats but of the possible cancers transitional cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed.
Carcinoma is the most common urinary bladder cancer. Three cases of transitional cell carcinoma in the cat and a review of the literature. A congenital form of the disease has been seen especially in Manx cats with rectalanal atresia and a sacral spinal deformity.
The urinary bladder is the most common site of lower urinary tract neoplasia in both dogs and cats 12. Cat bladder cancer is less frequent than other types of cancerHowever the most common bladder tumors in cats are carcinomas. Transitional Cell Carcinomas Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a prevalent type of bladder cancer in cats and more cats get diagnosed with transitional cell carcinoma than other types of bladder cancer every year.
However due to delays in diagnosis. They were received as post mortem specimens and were examined both macroscopically and microscopically. Long-haired cats are over-represented.
Chronic urinary tract infection UTI Cystitis. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Clinical signs are not.
The causes of bladder cancer are not known. When tumors appear in the urinary tract of cats the cells that line the urinary tract are affected. Lower urinary tract neoplasia is uncommon in dogs and cats though transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most common tumor of the lower urinary tract in both species.
2 of all canine tumors. Overview of Feline Urinary Bladder Cancer. In this paper a further three are presented.
Euthanasia was performed and necropsy revealed an extensive nodular thickening of the entire urinary bladder wall. The storage function of the bladder may allow for prolonged contact with carcinogens. Clinical signs vary with the degree of hypercalcaemia but around 50 of cats are asymptomatic.
1 2 Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most prevalent lower urinary tract cancer in dogs and considerable information regarding TCC is available for dogs including common anatomical. Tumors location vary greatly inside the bladder. The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites.
Hematuria Hematuria stranguria pollakiuria are common presenting signs.

Bladder Cancer In Cats Innovet Pet
Bladder Cancer In Cats Innovet Pet
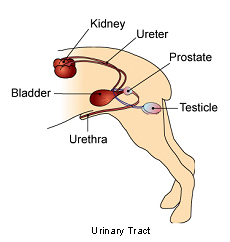
Urinary Tract Tumors Vca Animal Hospitals

Diagnosing And Managing Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
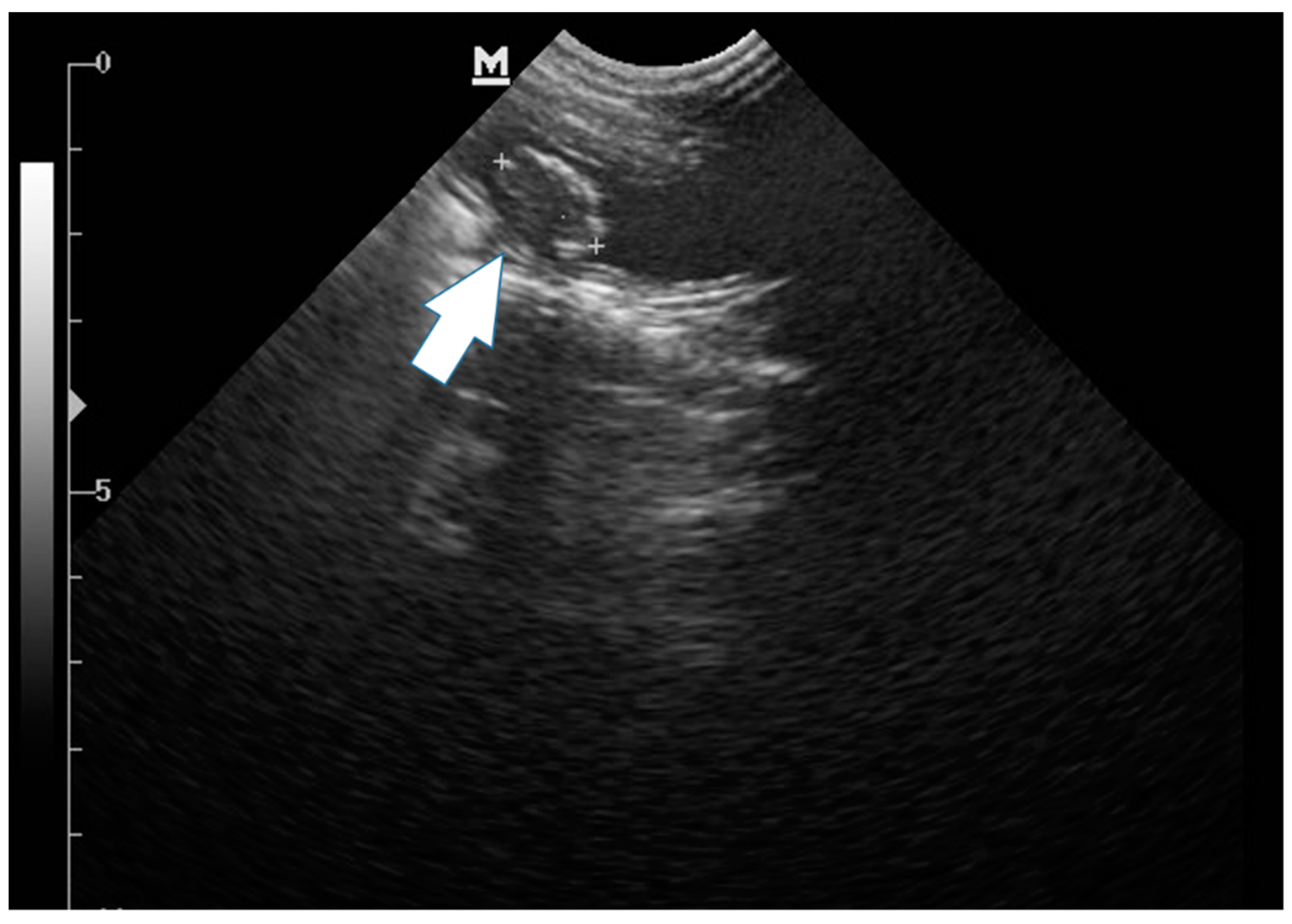
Veterinary Sciences Free Full Text Long Term Survival Of A Cat With Primary Leiomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder Html

Point Veterinary Surgery Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease Flutd If You Notice That Your Cat Has Difficulties Or Pain In Urinating Dysuria Increased Frequency Of Urination Pollakiuria Producing Little Or No

Feline Interstitial Cystitis A Cat Owner S Worst Nightmare Summeridge Animal Clinic

Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease Killarney Cat Hospital
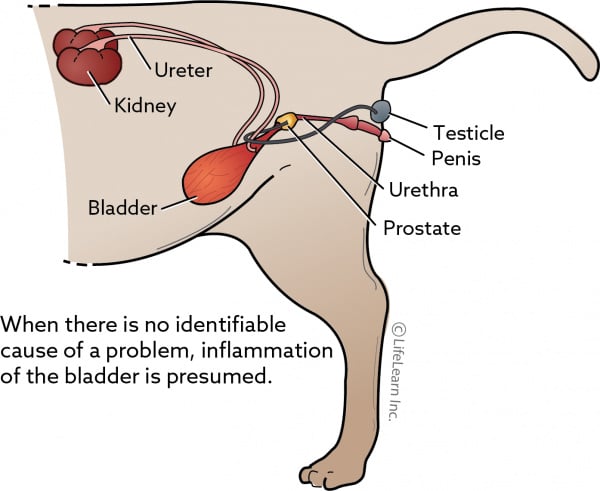
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis Vca Animal Hospitals
Feline Bladder Cancer Signs Prognosis And Treatment Homeoanimal Com

Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease Flutd International Cat Care
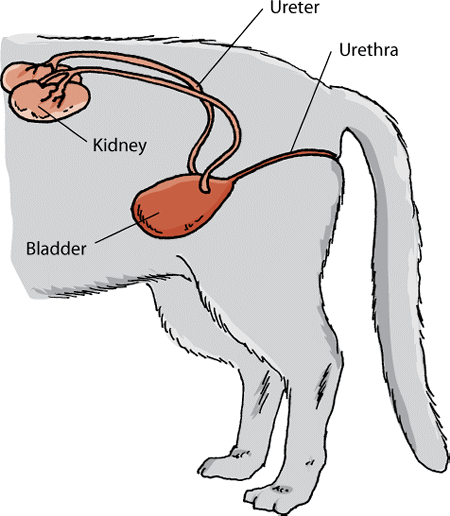
The Urinary System Of Cats Cat Owners Msd Veterinary Manual

Urinary Bladder Cancer Research College Of Veterinary Medicine Purdue University

Urinary Bladder Cancer In Cats Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost

Feline Kidney Anatomy Vet Tech Student Veterinary Tech Veterinary Medicine

Cat Can T Pee Signs He May Have A Urinary Blockage Daily Paws

